Data Governance Step by Step: Month 3
- Sash Barige

- May 24, 2022
- 2 min read
Updated: Nov 3, 2023

Month 3:
Data Governance Executive Presentation: This step is critical to the success of the program. All the preceding activities and this month's activities are geared toward convincing the senior leadership on the benefits of the data governance and to get them to sponsor and evangelize the program.
Data Inventory: Catalog and document all data assets within your organization, including sources, formats, and locations. This will be stored within the Data Catalog.
Data Dictionary: Develop a data dictionary to define data terms, standards, and metadata. This will be stored within the Data Catalog.
Finalize the data governance charter
Define Change Management Process
Define Learning Management Process
Data Governance Executive Presentation
Here's an example agenda for the executive presentation
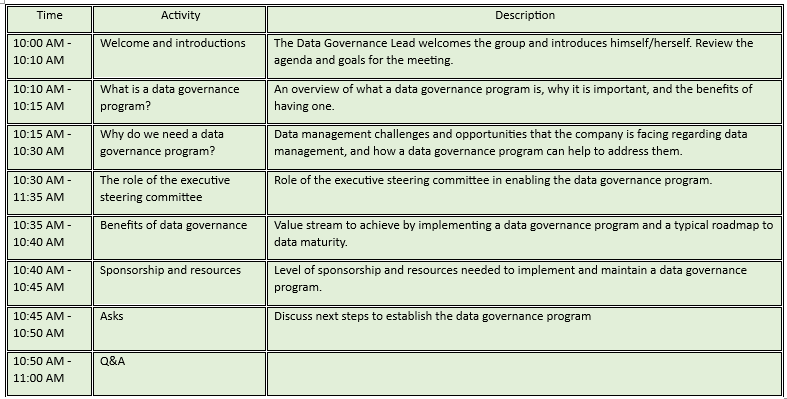
I had one of the executive prepped up prior to the meeting and had his backing and support during the presentation. After the meeting, you should follow up with the chief executives to answer any questions and to get their feedback on the plan. The data governance lead should also develop a detailed timeline and project plan for establishing the data governance program. One of the key immediate next step is to establish the Data Governance Council (DGC). Solicit recommendations from the executives and host a similar kickoff with the DGC members.
Data Inventory
Catalog and document all data assets within your organization, including sources, formats, and locations. This will be stored within the Data Catalog. Read my blog post on "Data Catalog for Data Governance" for further guidance.
Data Dictionary
Develop a data dictionary to define data terms, standards, and metadata. This will be stored within the Data Catalog.
Read my blog post on "Data Catalog for Data Governance" for further guidance.
A data dictionary for data governance is a centralized repository of information about an organization's data. It provides a single source of truth for data definitions, relationships, and usage guidelines. This can help to improve data quality, consistency, and accessibility across the organization. A data dictionary for data governance should include the following information:
In addition to the above information, a data dictionary for data governance may also include other information such as:
A data dictionary for data governance can be created and maintained using a variety of tools and technologies, such as spreadsheets, databases, or data governance software. The best tool or technology for the job will depend on the size and complexity of the organization's data environment. Here are some of the benefits of using a data dictionary for data governance:
A data dictionary is an essential tool for data governance. It can help organizations to improve data quality, consistency, accessibility, and security. |
Finalize the data governance charter
With the feedback and guidance from the DGC, finalize the data governance charter within the month. The charter will have the data governance purpose, mission, benefits, expectations, roles & responsibilities, data governance framework, a typical roadmap and expected long-term governance journey.
Read my blog post on "Establishing a Data Governance Charter" for further guidance.
Here is an example of a data governance charter: Data Governance Charter Version: 1.0 Date: May-11-2022 1. Purpose The purpose of this charter is to establish the data governance program for XYZ Corporation. The data governance program will ensure that the organization's data is managed in a consistent and effective manner, and that it is used to support the organization's business goals. 2. Scope The data governance program will cover all of the organization's data, regardless of its format or location. This includes data that is stored on-premises, in the cloud, or with third-party vendors. 3. Goals and Objectives The goals and objectives of the data governance program are to:
4. Roles and Responsibilities The following are the key roles and responsibilities in the data governance program:
5. Policies and Procedures The data governance program will be implemented and managed in accordance with the following policies and procedures:
6. Communication and Reporting The data governance team will communicate with stakeholders on a regular basis about the program's progress. The team will also report to the data governance council on a quarterly basis. 7. Executive Sponsorship This charter has been reviewed and approved by the executive leadership team of XYZ Corporation. 8. Approval This charter is approved by:
9. Signature [Signature] |
Define Change Management Process
Change management in the context of data governance is the process of planning, implementing, and managing changes to data governance practices within an organization. It is essential for achieving the successful adoption of new standards and policies, and for aligning culture and behavior towards a data-driven mindset. Change management in data governance culture and impact can be defined as the process of enabling people to adopt and implement new data governance practices in a way that is both effective and sustainable. It involves creating awareness and understanding of the changes, providing training and support, and managing resistance. The following are some key elements of change management for data governance culture and impact:
By effectively managing change, organizations can create a data governance culture that supports continuous improvement and enables them to leverage data as a strategic asset. Here are some specific examples of how change management can be used to manage data governance culture and impact:
Organizations can use change management to create a data governance culture that supports continuous improvement and enables them to leverage data as a strategic asset. |
Define Learning Management Process
Learning management is the process of creating, delivering, and managing learning activities and resources to achieve specific learning outcomes. In the context of data governance culture, data literacy, employee training, and support, learning management can be used to:
To establish learning management to manage data governance culture, data literacy, employee training, and support, organizations should consider the following steps:
Here are some specific examples of how learning management can be used to manage data governance culture, data literacy, employee training, and support:
By implementing a learning management program, organizations can help employees to develop the knowledge and skills they need to support data governance, build data literacy, and make better decisions. This can lead to a more data-driven culture and improved organizational performance. |
Sash Barige
May/25/2022




Comments